In the world of advertising, incentives play a powerful role in capturing the attention and influencing the behavior of consumers. Whether it’s a discount, a free gift, or a limited-time offer, these incentives have a profound impact on our decision-making process. But have you ever wondered what lies behind the effectiveness of these tactics? This article will explore the psychological principles that underpin the use of incentives in advertising and shed light on why they can be so persuasive.

This image is property of www.verywellmind.com.
The Power of Incentives
Incentives play a powerful role in advertising, as they tap into our innate psychological principles and biases. By understanding these principles, advertisers can effectively leverage incentives to drive consumer behavior and achieve their advertising goals. In this article, we will explore the definition of incentives, their role in advertising, and the psychological principles that underlie their effectiveness. We will also discuss how incentives can be used in a responsible and ethical manner, and provide examples of incentive-based advertising campaigns.
The Definition of Incentives
Before delving into the psychological principles behind incentives, let’s first define what they actually are. In the context of advertising, incentives refer to rewards or benefits that are offered to consumers as a means of motivating them to take a desired action. These actions can range from making a purchase, signing up for a service, or simply engaging with an advertisement. Incentives can come in various forms, such as discounts, freebies, rewards programs, contests, or exclusive access to certain products or experiences. The key characteristic of incentives is that they provide consumers with added value or a sense of gain for engaging in the desired behavior.
The Role of Incentives in Advertising
Incentives are an integral part of advertising strategies because they tap into our underlying psychological principles and biases. By offering consumers a reward or benefit, advertisers are able to trigger certain cognitive and emotional responses that influence our decision-making process. Incentives provide an extra push to overcome any hesitation or resistance a consumer may have in taking the desired action. They can create a sense of urgency, build trust, and foster a positive emotional connection with a product or brand.
Psychological Principles
To better understand the effectiveness of incentives, it is essential to explore the psychological principles that underlie their impact. Let’s delve into some of the key principles that advertisers leverage to maximize the effectiveness of incentives:
The Principle of Reciprocity
The principle of reciprocity refers to the innate human tendency to feel obligated to give back when we receive something. By offering a reward or benefit, advertisers can tap into this principle and create a sense of indebtedness in consumers. This can lead to increased engagement, loyalty, and positive word-of-mouth.
The Principle of Scarcity
The principle of scarcity taps into our fear of missing out on valuable opportunities. When an incentive is presented as limited in quantity or time, it triggers a sense of urgency and motivates consumers to take immediate action. By creating a perceived scarcity, advertisers can drive demand and promote sales.
The Principle of Social Proof
The principle of social proof revolves around our tendency to look to others for guidance on how to behave. When incentives are positioned as something that others have already benefited from, it creates social validation. Consumers are more likely to trust and follow the actions of others, especially when they perceive those actions as beneficial.
The Principle of Authority
The principle of authority asserts that we have a natural inclination to trust and obey figures of authority. By associating incentives with credible experts, influencers, or well-known brands, advertisers can leverage this principle to enhance the perceived value and credibility of the incentives. This, in turn, increases the likelihood of consumer engagement and action.
The Principle of Consistency
The principle of consistency highlights our desire to act in alignment with our past behavior or commitments. By emphasizing the alignment between the desired behavior and consumer values, advertisers can reinforce the perceived benefits of incentives. This consistency can be harnessed to influence consumer attitudes and increase the likelihood of taking the desired action.
The Principle of Liking
The principle of liking centers around our preference for people and brands that we find attractive or relatable. By showcasing incentives in a way that appeals to an individual’s personal preferences, values, or aspirations, advertisers can tap into this principle to strengthen the emotional connection between the consumer and the incentive. This emotional bond can significantly impact consumer behavior.
Incentives and Cognitive Bias
In addition to psychological principles, incentives also interact with various cognitive biases that influence our decision-making process. Let’s explore some of the cognitive biases that incentives can exploit:
Anchoring Bias
Anchoring bias refers to our tendency to rely heavily on the first piece of information we receive when making a decision. By providing consumers with a high-value incentive upfront, advertisers can anchor their perception of the product or service’s value. This biased perception can influence subsequent evaluations and increase the likelihood of positive consumer behavior.
Framing Effect
The framing effect occurs when our decisions are influenced by how information is presented to us. By framing incentives as gains rather than losses, advertisers can tap into our aversion to losses and motivate consumers to take the desired action. This approach capitalizes on our tendency to be more motivated by the fear of missing out on a gain than the potential regret of missing out on a loss.
Loss Aversion
Loss aversion refers to our tendency to place greater value on avoiding losses than acquiring gains. This bias can be leveraged by presenting incentives as opportunities to avoid losing out on valuable rewards or benefits. By emphasizing the potential losses consumers may experience by not taking the desired action, advertisers can effectively tap into this bias and drive consumer behavior.
Using Incentives Effectively
To use incentives effectively in advertising, it is crucial to consider the following factors:
Understanding the Target Audience
A deep understanding of the target audience is essential for designing and implementing effective incentive-based advertising campaigns. By conducting thorough market research and analyzing consumer behavior, advertisers can tailor incentives to align with the specific desires, needs, and preferences of their target audience. This personalized approach increases the relevance and appeal of the incentives, thereby maximizing their effectiveness.
Aligning Incentives with Advertising Goals
Incentives should be carefully aligned with the overall advertising goals of a campaign. Whether the objective is to increase awareness, boost sales, or enhance brand loyalty, incentives should be designed to directly contribute to these objectives. By ensuring a clear alignment between incentives and advertising goals, advertisers can optimize the impact of the incentives and maximize their return on investment.
Creating a Sense of Value
To effectively leverage incentives, advertisers must create a perception of value in the minds of consumers. This can be achieved by highlighting the unique features, benefits, or advantages of the incentives. Additionally, presenting incentives as exclusive or rare enhances their perceived value. By effectively communicating the value of incentives, advertisers can stimulate consumer interest and motivate action.
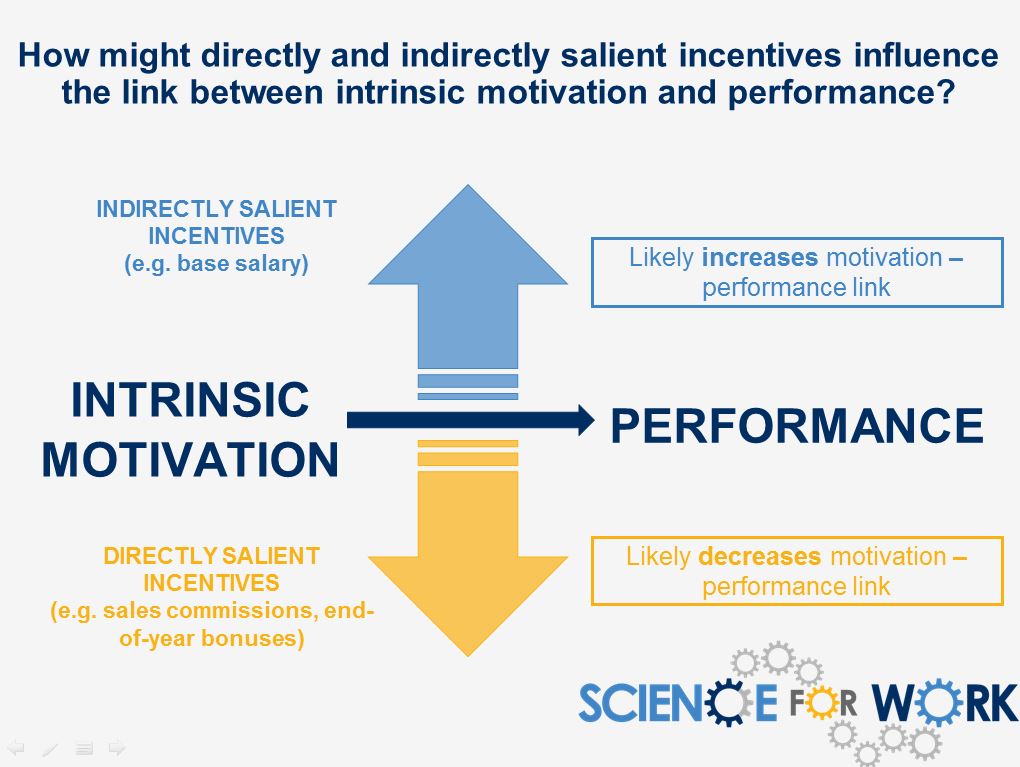
This image is property of scienceforwork.com.
Ethical Considerations
While incentives can be powerful tools in advertising, it is essential to approach their use with integrity and ethical considerations. Advertisers must prioritize transparency and honesty in their messaging to avoid misleading or deceiving consumers. Clearly communicating the terms and conditions of incentives, including any limitations or exclusions, ensures consumers make informed decisions. Furthermore, it is crucial to avoid manipulative tactics that exploit vulnerable individuals or engage in deceptive practices that erode trust.
Examples of Incentive-based Advertising
The successful implementation of incentive-based advertising can be witnessed across various industries. Some popular examples include:
Discounts and Coupons
Offering discounts or coupons is a common incentive strategy used by retailers and online merchants. By providing consumers with the opportunity to save money on their purchase, these incentives drive immediate sales.
Free Trials and Samples
Free trials and samples are widely used by companies offering products or services that benefit from consumer trials. By providing consumers with a risk-free opportunity to experience the offering, businesses can increase brand exposure, build trust, and ultimately convert them into paying customers.
Reward Programs
Reward programs, such as loyalty cards or point systems, are prevalent in industries like airlines, hospitality, and retail. These programs incentivize repeat business and foster customer loyalty by offering exclusive discounts, perks, or freebies based on accumulated points or purchases.
Contests and Sweepstakes
Contests and sweepstakes leverage the excitement and thrill of competition to incentivize consumer engagement. By offering the chance to win valuable prizes or experiences, advertisers create a sense of anticipation and motivation to participate.

This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
The Future of Incentive-based Advertising
As technology continues to advance and consumer behaviors evolve, the future of incentive-based advertising holds immense potential. Here are a couple of noteworthy avenues:
Advances in Technology
Technological advancements, such as augmented reality and virtual reality, present new opportunities for immersive and interactive incentive-based advertising. These emerging technologies can enhance the sensory experience of incentives, creating a more memorable and engaging connection with consumers.
Personalization and Customization
With the increasing availability of data and advanced analytics, advertisers can leverage personalization and customization to enhance the effectiveness of incentives. Tailoring incentives based on individual consumer preferences, past behaviors, or location can significantly increase their relevance and impact.
In conclusion, incentives are a powerful tool in advertising that tap into our psychological principles and biases. By understanding these principles and leveraging cognitive biases, advertisers can effectively drive consumer behavior and achieve their advertising goals. However, it is crucial to approach the use of incentives ethically and responsibly, prioritizing transparency, honesty, and the avoidance of manipulative tactics. With a deep understanding of the target audience, clear alignment with advertising goals, and the creation of value, incentives can be leveraged to create impactful advertising campaigns. The future of incentive-based advertising holds exciting opportunities for innovation and enhanced personalization, driven by advances in technology and consumer insights.


